Abstract
Purpose – The purpose of this paper is to design a smart library that is combined with cloud-computing and Big Data technology to effectively integrate information resources based on information and smart service platforms.
Design/methodology/approach – The design for the construction of a smart-library-system platform is presented based on Big Data, the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and other new and emerging technologies.
Findings –This paper defines a smart library based on cloud platform. Based on the information and intelligent service platform, this paper proposes the construction and application of the smart library platform, and analyzes the system framework and key technologies of the smart library. The system effectively integrates information resources and expands the research in the field of smart library system based on cloud platform, further enhances the application effect of smart library based on cloud platform, and establishes a perfect big data platform system of smart library.
Originality/value – A smart library system enables libraries to operate more intelligently and improve service quality, thereby enhancing the experience of library users.
Keywords Cloud platform, Smart library, Big Data, Visualization technology, Smart library system, Smart service
Paper type Research paper
Introduction
The World is experiencing a new industrial revolution, centered on intelligence. Linking Big Data, the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and other new and emerging technologies can potentially improve the lives of all. This combination of data and technology is already changing the libraries. This paper presents a design for a smart library system based on a cloud platform which promises to improve the utilization of resources, the delivery of services, and the enhancement of library users. The smart library is based on a ubiquitous information network, intelligent-sensing technology, and the information-security infrastructure required to transparently and fully acquire library resources and massive amounts of user data. It provides library users with shared information, creating library informatization application of knowledge sharing, efficient service, and convenient use.
Concept and characteristics of cloud platforms
The cloud-computing platform (hereinafter referred to as the cloud platform) is the core of cloud services. Without cloud platforms there are no cloud computing and cloud services. At present, there are four influential mainstream open-source software platforms in the cloud-services industry, namely OpenStack, CloudStack, Eucalyptus, and OpenNebula (Sun, 2014).
With the continuous application of new technologies, such as the Internet of Things, Big Data, and cloud computing, how to effectively use the cloud platform to collect and cross-match different types of data is the key to shaping the future library. When data from various sources are collected on a cloud platform, the “beating” of the data represents the pulse of the library.
Intelligent management of the library is realized through mapping of the virtual collection to the physical library.
Advantages of smart library systems based on cloud platforms
The ultimate goal of the smart library is that the library’s management and services can be intelligently completed, reaching the smart state (China Library Weekly, 2017), which is a state that human intervention is not necessary. A cloud platform can effectively achieve the goal of an smart library. Interconnectivity, high efficiency, and convenience (Wang, 2014) are the main features of smart libraries, and a cloud platform can provide strong support for the realization of the smart-library goal. The core of the cloud platform is the integration and utilization of Big Data, which can optimize and integrate data resources. Cloud platforms can unify data standards, data management, and data maintenance to optimize software and hardware resources and improve overall resource allocation.
A cloud platform needs to have the following five characteristics: resource integration, ubiquitous network access, quantifiable services, rapid and elastic deployment, and on-demand services. Among these five, ubiquitous network access and resource integration are fundamental prerequisites, equivalent to the foundation of a house. The other characteristics determine the level of management and application of the cloud platform. With the development of intelligent technology, the wide application of Big Data, the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and the support of intelligent concepts, libraries can rely on advanced cloud-platform technology to build a smart management system to improve service efficiency and service quality.
Implementation of smart service management
In the smart library system, by building a unified Big Data cloud infrastructure platform, the cloud-platform technology can be used to flexibly find various data in the library and integrate resources to assist the library services in time according to the data-information cloud. Additionally, the library’s management department can mine the library users’ demands through the data-driven platform, so that the library’s service meets its users’ needs more closely. Enabling library users to become the main entity of library innovation services and participate in the process of innovative services facilitates their use of library data. Thus, the sustainable development of libraries under the society environment of innovative knowledge, characterized by both library user and service innovations, can be achieved.
Providing diversified library services
A cloud-based smart-library system will render smart services free of blind spots and provide library users with efficient and stable smart-library services. In such a system, administrators can monitor places in the library including offices, borrowing rooms, reading rooms, and study rooms, in order to fix (potential) problems timely and accurately. In addition, supported by the cloud platform, the smart-library system can realize digital book positioning and service on demand, and use cloud technology to quickly send information in the system, saving service time and improving efficiency.
Construction of library quantitative service system
For a library user, a library’s service is intangible, and the evaluation of its service quality is difficult. The smart-library system provides more support and assurance for the evaluation of library service quality. Using technologies such as Big Data, cloud computing, and visualization, the system can clearly define the service content, scope, efficiency, and response-time. Intangible services are presented to library users with quantifiable indicators. Library users can choose the services that meet their needs through the service content and corresponding commitments in the system (Jia, 2014).
Design of smart-library system based on cloud platform
The effectiveness of the informatization application of a smart library is enhanced by cloud-platform technology. Supported by the informationalized and smart service platform, a sound smart-library management system that integrates the environment, equipment, resources, and library users can be established. The cloud platform provides service support for the smart-library system, including data support, information-system support, consolidated identity authentication, information retrieval, and secure information delivery. At the same time, data and application services are provided to library users through a data-exchange portal. Through this portal, library users can utilize the library’s resources, downloading, displaying, and re-integrating as needed. In addition, resources can be uploaded to the Big Data foundation cloud platform of the smart library through this portal. The smart-library management system includes data collection, data management, business analysis, service management, and information dissemination. Figure 1 displays the overall architecture of a cloud-based smart library system.
Data collection
Data collection in the smart-library system is a data-import solution based on large-capacity messages and events. The scope of data collection is not restricted to the information about books. Various data, including library user-identity information, user-account data, various equipment information, library space and environment information, and even a third-party database, are collected by the smart-library system. The system is oriented to different formats of structured and unstructured data, providing a variety of data-source management, format conversion, and temporary storage services of raw data. Its core capabilities include data-channel management, data-source management, and data-format conversion.
Data management
A smart-library system based on a cloud platform can manage the latest resource (such as information on the collection in the library, circulation, and bibliographic and transaction data), environmental, and service information. Heterogeneous systems are audited in accordance with uniform standards, and only data that have passed the audit can be displayed. The data-management function not only stores various data, but also enriches the database system for daily operational data. The data warehouse of historical and current data are centralized and integrated. Further, the module also provides security-policy execution for data access. Under the OData protocol, the corresponding data are published and updated through the Library Service Management and Information Release components as the basis of the information service. Therefore, the intelligent scheduling of the physical location of the collection, book status tracking, and network-security monitoring can be easily realized, ensuring data security and privacy. Data of bibliography, collections, circulation, and transactions can be collected in real time through the cloud platform, and then uploaded to the corresponding smart-library platform through the network. Finally, the data-optimization and tracking processes are realized.
Business analysis
The smart-library system statistically classifies and relevantly integrates data from different sources. The integration includes the application systems, including interview and consulting data, literature collection, data-resource retrieval, information reference, education and training, conferences and exhibitions, and digital processing. The smart library system has a search engine for querying data statistics, forecasting, and business intelligence for structured, unstructured, and streaming data. On this engine, using preset algorithms, new intelligent analytics can be quickly built and deployed; and new statistical, predictive, and multi-dimensional analysis results can be published instantly. The business-analysis function can analyze many types of data, including library-collection resource, library-space, business-management, library-environment, library user visits, library user accounts, reading promotion, and knowledge service.
Through the integration and intelligent analysis of various business data, the library can optimize resource allocation and business processes, and improve the level and service of quality. Moreover, such integration provides more robust support for the formulation and effectuation of library strategic plans. For example, problems existing in the library’s collections can be identified in a timely manner via the analysis of interlibrary-loan data, allowing resources to be appropriately added/deleted. Following the analysis of library user-traffic data, the number of visitors to the library at each hour of the day, the cumulative number of visitors per month, and the cumulative number of visitors per year can be obtained. Collation and analysis of the book-loan and search-and-retrieval data can help accurately match resources with library user demand, so services can be effectuated using personalized library user data. An analysis of library users’ consulting requests and various activity data, user questions and actual needs can be identified, and the library can implement relevant and targeted training and reading-promotion activities (Chen, 2015). Through real-time monitoring and analysis of data in offices, borrowing, reading, and information-sharing areas, the space inside the library can be optimally utilized.
Service management
The smart-library system is a public and comprehensive service platform. Through data, it mainly provides cloud-computing resource management, multi-level data exchange, application-support platform (basic and application components), and business-application integration services. At the same time, it adopts cluster management to realize resource integration, intensive display, and fast acquisition (Zheng, 2014). The system performs centralized service presentation based on the results of data management and business analysis. With the cloud library as the gateway for all access services, through the integration of physical libraries and online library platforms, the main content provides a variety of services for the entire Big Data platform, including customizable public services, virtual consulting, one-stop search, basic borrowing, information navigation, space sharing, and joint user authentication.
Information dissemination
The smart-library system provides a manageable release channel of the Big Data platform. The information and intelligent analysis results can be obtained according to their own needs through different release channels and in different data formats, including push channels, active acquisition channels, channel-management services and channel policies, and library geographic information systems.
A library publishes information through channels including websites, mobile phone text messages, QQ, WeChat, Weibo, and community platform. The smart-library system can collect and integrate the information of each channel to achieve comprehensive coverage of various media resources. It displays various kinds of literature resources of the library to its users, such as book and magazine collections, newspapers, multimedia resources, and books at the library’s branches, and also according to a library user’s personalized information, such as historical borrowing information, gender, major, hobbies, and borrowing time.
The system can also display popular books and multimedia digital resources clearly to library users through intelligent association, Big Data mining, and visualization (Zheng, 2016). Additionally, the system allows library users to submit their views through the platform, encourages library users to participate in decision-making, share opinions, and innovate collaboratively. Thus, interaction, communication, and cooperation between libraries and library users can be achieved. By relying on the users, for the users, and serving the users, a smart library system integrating wisdom from cyberspace can be achieved.
Implementation of a smart-library system based on cloud platform
The utilization, analysis, and decision-making services of a smart-library management system for Big Data can provide decision support and service guarantees for library management, and bring more efficient service, modernization, and stronger innovation to library operation. The smart-library system can affect a unified information-resource-sharing infrastructure, provide unified data support for library business applications, and build a clear information-resource-management structure to achieve the purpose of unified control, effective sharing, and rational use of data. It can also build a model to lay the foundation for a unified data view and data that support for library business. The system can achieve the main functions of cross-domain data collection, real-time situational awareness, smart-service integration, and Big Data statistical analysis and display.
Cross-domain data collection
A smart-library system is a comprehensive service based on data sources, which includes library-equipment data (e.g., self-service borrowing systems, access control systems) as well as manual filing documents, integrated service data, and visual traffic-management-system data (Lai et al., 2015). Through a smart management system, the service and management model of cross-system application integration, cross-department information sharing, cross-database network interoperability, cross-media deep integration, and interlibrary logistics express can be established across different literature information institutions and between various documents. Therefore, data collection across types, departments, systems, and libraries can be achieved. The smart-library system includes both OPAC-based system resources and the integration of commercial database resources and the digital resources built by the library. Additionally, the information-resource-application system, the resource database system, and the security-management system can be integrated and managed.
Real-time situational awareness
A smart-library system has functions such as management visualization, real-time monitoring of security warnings, remote-supervision functionality, and real-time location-sensing response. These functions help to improve the intelligence level of the library (Guo, 2015). The system can provide library users with 24-h online service. Library users can access the library’s electronic resources, book-renewal reservations, seat-space reservations and other services at any time and any place through virtual private networks. Library users can also keep track of information, such as library notices, news updates, and interlibrary resources. In addition, a smart-library system has good compatibility and is applicable to all common mobile terminals, such as mobile phones, and tablets. Library users can interact with library systems and terminals according to their preferences, while enjoying library resources and smart service.
Smart-service integration
In the traditional digital-library user-service model, the library’s service scope is limited to the home library. A ubiquitous smart library can combine different types of libraries and library users, using the smart-service network built by the Internet and cloud platform to bring structured network services to library users, and making the relationship between libraries and library users closer (Chen and Xu, 2015). Based on the concept of integrated design, open management, and humanized service, and the principle of diversity of functional layout and diversification of document carrier, a smart-library system implements the integration service of collecting, checking, borrowing, reading, and participating. The reform of service is reflected in three connections: between things; between things and people; and between people.
With the help of the RFID technology and the interface technology of the Internet of Things, omni-directional interconnection can be achieved, which includes the connections between book and book, library and library, various resources and the corresponding terminals of the library, and between multi-terminal devices. Therefore, the cluster management of the library-collection resources can be realized (Shi, 2017). In this paper, books include traditional print and digital and network-based multimedia documents. With the help of technologies such as mobile terminals and Internet of Things sensors, information on environment, rooms, various appliances, and devices are interconnected with people. After the seamless connection between librarians and library users, and between users and users based on smart technology, library-collection resources can be effectively provided and to meet the library users’ needs. The library provides multiple types of learning spaces and is equipped with corresponding collaboration devices to conveniently provide information sharing, communication, and interaction between library users.
Big Data statistical analysis and display
A smart-library system makes full use of the modern information technology of a cloud platform. It not only can realize the intelligent and self-service library, and networking of the book-collection system, retrieval system, business process, and user service, but can also realize the intelligent visual statistics of Big Data. Through the comprehensive use of electronic information technology, computer technology, and modern communication technology, library equipment, business processes, resources, users, buildings, etc. are automatically monitored and scheduled to provide library users with a high-quality, safe, comfortable, and efficient information service environment. These are mainly reflected in the following aspects.
Library Big Data statistics
A smart-library system can gather the following comprehensive statistics on library users entering the library: (1) accurate user traffic at different times; (2) visitors to the library from single-door access and multiple-door access at the same time; and (3) the direction of users entering and leaving the same straight-line area. For example, if library users come in and out at the same time on the same line, the system can count (and display) the in and out separately. For example, the three-dimensional images of user distribution on the hotspot area can indicate the library user density of each region with different colors and color depths. This gives an early warning to remind the library to add service personnel when an overflow appears and arrange library activities accordingly, while reducing overcrowding and seat occupation ensure safety and stability.
Analysis of Big Data behavior
A smart-library system is interfaced with the business system to integrate circulation data. It can count the number of borrowers on a given day, the number of applicants, the number of people reading, and the use of seats (Figure 2). These data reflect library users’ borrowing behavior, reading behavior, and reading habits. The library can make targeted adjustments to book procurement, collection, and library construction according to data trends. For example, the library can adjust the spatial layout of the library according to the users’ reading data and changing trends, and provide a basis for library user-behavior analysis. This not only improves the circulation and utilization of books, but also expands user services, and improves service quality. In addition, the analysis of library user borrowing and reading behavior by the system can reconfigure the numbers and types of books purchased, and the amount of copies.
Big Data visualization display
Combined with the data in the library-automation system, the analysis charts of passenger traffic and borrowed data can be provided. The real-time data, analysis charts, and renderings of the location in the library can be displayed through large screens (Figure 3), so that library users can see the library-service situation at a glance. Reflecting the library users’ utilization of library resources through objective statistics enables the library to optimize decision-making in resource procurement, space planning, and staff layout.
Conclusions
In the report of the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party, a smart society is regarded as one of the development goals of accelerating the construction of an innovative country (Qing, 2017). With the rapid development of digital, networking, and intelligent technologies such as Big Data, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things, libraries need to reform and adjust their resources, technology, services, and personnel. The design of a smart-library-system platform is presented in this paper as a reference for the construction of such a system.
In the future, we plan to conduct in-depth research to determine whether new applications can be tried and explored in such a system; as well as discuss potential, new technologies; whether the system functions are sound enough; and what problems/obstacles may arise in implementation.
References
Chen, W. (2015), “Smart analysis of smart libraries in Big Data environment,” Library and Information Service, Vol. 59 No. 12, pp. 49–52.
Chen, Y. and Xu, L. (2015), “The construction of smart library for users' ubiquitous smart service,” Library Journal, Vol. 34 No. 8, pp. 4–9.
China Library Weekly (2017), “The future of the library - "Smart Library" (Part One),” available at: http://www.sohu.com/a/146221061_748548 (accessed 5 June 2017)
Guo, S. (2015), “Design and implementation of universities smart library information service system,” Master's thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding.
Jia, F. (2014), “Building a library smart service system in the network age,” Library Journal, Vol. 36 No. 2, pp. 98–100.
Lai, Q., Huang, L. and Liu, J. (2012), “Building a smart library with the "Internet of Things" and "Cloud Computing" technology,” New Century Library, No. 5, pp. 46–49.
Qing J. (2017), “The 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China opened, Xi Jinping made a report on behalf of the 18th Central Committee (live full text),” available at: http://www.china.com.cn/cppcc/2017-10/18/content_41752399.htm (accessed 18 October 2017)
Shi, B. (2017), “RFID-based smart library management system,” Master's thesis, Jilin University, Changchun.
Sun, J. (2014), “Competition: The advantages of four open source cloud platforms,” China Informatization, No. Z3, pp. 27–29.
Wang, S. (2014), “On three main features of the smart library,” The Journal of the Library Science in China, Vol. 38 No. 6, pp. 22–28.
Zheng, L. (2016), “Research on the construction of library smart wall system based on Big Data,” Library Science Research, No. 21, pp. 31–35.
Zheng, Z. (2014), “On the construction of library's smart service system,” Journal of Library Science, Vol. 36 No. 12, pp. 92–94.
Figure legends
Figure 1. Overall structure of smart library system
Figure 2. Analysis of multiple types of data
Figure 3. Data analysis and display

Figure 1.
People entering the library on a given day: 1155
People borrowing books on that day: 340
People returning books on that day: 215
People applying for library cards on that day: 60

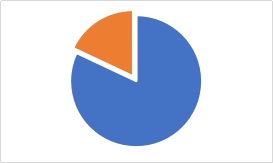
Percentage of people borrowing books 29.44% Percentage of people returning books 18.61%
The blue part is the number of people who have not borrowed books, the orange part is the number of people who have borrowed books, the blue part is the number of people who have returned books, and the orange part is the number of people who have not returned books.
Figure 2.

Figure 3.

